Sample Size For Pilot Study
Sufficiently precise estimates of mean and variance julious sa.
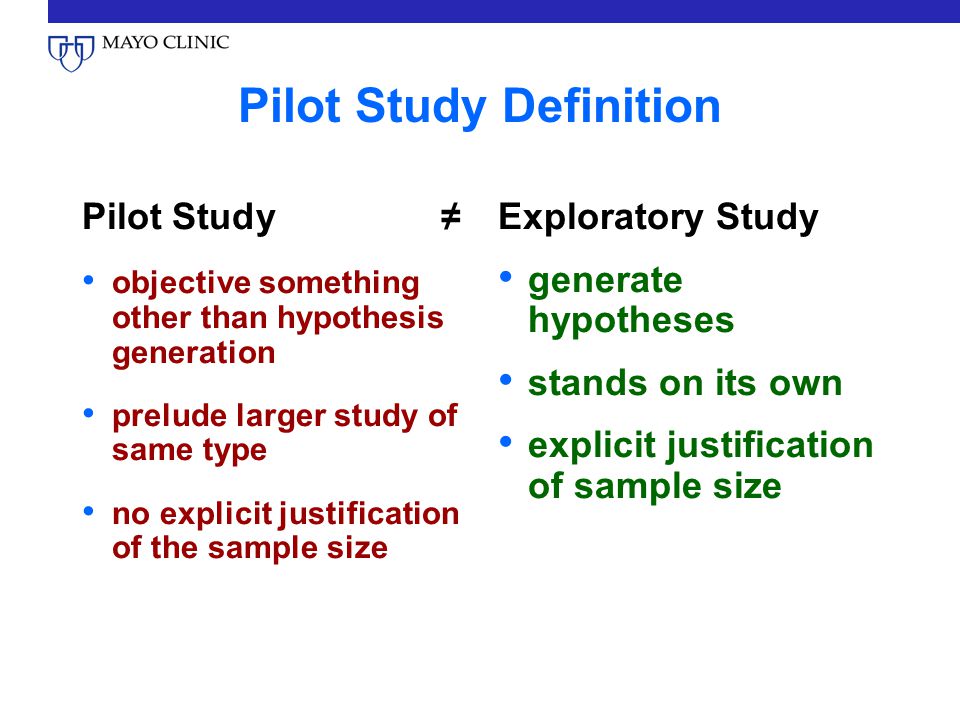
Sample size for pilot study. Sample size for pilot studies. Having the need to engage in a sample size justification for a pilot study recently and consistent with frank s prior aug 2018 comment regarding precision i came across the following march 2018 reference that others may find helpful. 10 participants with the outcome for each predictor logistic regression. William barry mitch 2013 opined the sample size for pilot study should be between 1 1 5 of the sample size to be used in study.
Sometimes the level of confidence the researchers has about which the pilot test option. Sample size to pilot study can be 5 of the total sample size of the actual study in the quantitative study. Cooper and saunder 2016 suggested 25 100 subjects. These results are for the total sample size of two group studies in which the sample sizes of each group will be equal.
Sample size of 12 per group rule of thumb for a pilot study. Pilot studies are experiments that aim at providing a range confidence interval of values for a parameter of interest it may be the standard deviation of a given parameter its mean the proportion of individuals fulfilling some condition. Pilot study sample size rules of thumb introduction this routine presents rules of thumb for finding an appropriate sample size for a pilot study in which the outcome is a continuous measurement. There is little published guidance concerning how large a pilot study should be.
2005 4 4 287 291 rule of 10 binary outcome. It should also be based on the same inclusion exclusion criteria as the main study. It is important that the sample for a pilot be representative of the target study population. One of the goals of a pilot study is to identify unforeseen problems such as ambiguous eligibility criteria or misinterpretations of questionnaire items.
Rules of thumb rule of 12 continuous outcome. The formula below can be used to calculate the sample size needed to be able to identify with a chosen level of confidence problems that may arise with a given probability.